Types and Advantages of Solar Tracking System

Solar tracking systems are a form of mechanical racking that commonly incorporates motorized components. The objective is to maximize energy capture from solar arrays throughout the day. This is achieved by mounting PV modules on a structure capable of precise rotation, enabling them to align with the sun's trajectory. By optimizing the angle of incidence, the tracking system can significantly enhance energy production.
Trackers utilize advanced sensors and processors to ensure the highest efficiency in capturing sunlight while equipped with algorithms capable of real-time solar tracking. In this article, we will introduce different types of solar tracking systems along with their advantages and disadvantages.
What Are Solar Trackers and How Do They Work?
Solar trackers are devices outfitted with PV panels, capable of accurately tracking the Sun's trajectory throughout the day. The efficiency with which solar panels convert sunlight into electricity is significantly influenced by the angle of incidence, which is the angle at which the Sun's rays intersect the surface of the solar panel. A narrower angle of incidence facilitates a higher energy yield from the photovoltaic panel. Solar trackers assist in minimizing this angle by diligently adjusting the orientation of the solar panels, ensuring that sunlight strikes them perpendicularly.
The solar tracking apparatus comprises an array of components, including Photovoltaic Cells, Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC), signal processing units, sensors, electromagnetic and mechanical motion control modules, alongside power supply systems. The activation of the panel is triggered by the intensity of sunlight, which is then relayed to the sensors. Following this, the sensor output is transmitted to the PLC.
Subsequently, the PLC conducts a comparative analysis and generates a corresponding output to actuate the motor. This motor, in turn, repositions the panel to align it optimally towards the sun, ensuring a perpendicular orientation. A solar panel that maintains a precise perpendicular alignment with the sun invariably generates a higher power output compared to one that does not hold this orientation.
Types of a Solar Tracker
Solar tracking systems can be categorized based on their mode of motion. There are two horizontal axes and one vertical axis for a moving surface. By rotating the surface around each axis, known as tilting, the optimal angle for capturing maximum sunlight can be achieved.
Single-axis tracking refers to the rotation of the surface around one axis. Dual-axis tracking refers to the rotation of the surface around two axes simultaneously.
Single-axis Solar Trackers
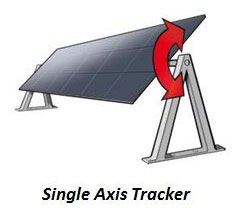
A single-axis tracker is a solar panel adjustment device rotating around a single axis, typically aligned in the North-South directions. This device facilitates the movement of solar panels in synchronization with the sun's trajectory, enabling them to track its path from East to West as it rises and sets.
Single-axis solar trackers enhance solar panel performance by optimizing sun exposure, particularly during spring and summer when the sun is higher. However, their effectiveness diminishes further north due to greater solar angle variance between summer and winter. Additionally, performance drops during times when the sun is in a more horizontal position. In higher latitudes, vertical axis trackers, which can adjust to the sun's lower path, are more effective.
While single-axis solar trackers require higher upfront installation costs and ongoing maintenance, they can boost the efficiency of your solar system by 20% to 30%. This notable feature allows for a substantial augmentation in the collection of solar energy throughout the day, thereby compensating for these expenditures in a relatively short period.
Dual-axis Solar Trackers
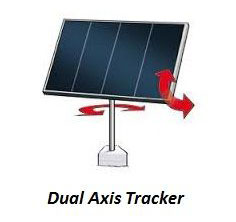
A dual-axis solar tracker enables your panels to rotate on two axes, oriented both north-south and east-west, denominated as the "primary axis" and the "secondary axis." Employing sophisticated algorithms and sensors, it adeptly tracks seasonal alterations and variations in the sun's altitude in addition to the sun's general daily motion. This ability to acclimate to the annual seasons markedly optimizes solar energy production, ensuring steadfast and reliable performance irrespective of climatic conditions.
Dual-axis trackers may be well-suited for specific commercial properties – they can generate up to 45 percent more energy than conventional static panels. This enhanced energy production aids businesses in developing sufficient power to sustain their operations, even with limited rooftop space. Conversely, utility-scale installations typically do not necessitate dual-axis configurations owing to their location on expansive plots of land, devoid of the stringent spatial constraints encountered in commercial rooftop spaces.
Although dual-axis solar trackers are more costly, they are ideal for commercial solar projects with limited space and many users.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Solar Trackers

A paramount advantage of employing a solar tracking system lies in its capacity to augment electricity production, in contrast to a comparably sized static solar plant. Typically, the performance of a plant fitted with a single-axis solar tracker can be improved by 20% to 30%. Installing a dual-axis tracker propels the performance further by 5 to 10 percent, culminating in a performance efficiency escalation of up to 40%. This is particularly impactful in high latitude locales where the sun's positioning in the sky varies substantially between the summer and winter months, rendering a dual-axis tracking system a productive method to maximize solar yield.
While trackers can increase the amount of electricity a PV plant generates, certain considerations still warrant attention. Tracking systems entail significantly higher installation and maintenance expenses than static solar establishments. Due to the sophisticated technology and movable components intrinsic to solar trackers, the initial investment cost is correspondingly increased. The more complex a system is, the more likely it is to result in more maintenance and thus additional costs over time.
A notable drawback of solar trackers is their unsuitability for rooftop solar installations, which are typically favored for their lower installation costs and ease of maintenance. Tracking necessitates a substantial spacing between panels to accommodate movement, markedly restricting the number of panels that can be deployed and rendering the system excessively hefty for rooftop applications.
Are Solar Trackers Worth it?
Solar trackers are not worth the investment for most residential installations because they add to the system's upfront cost and may need to generate more energy to offset the cost. However, solar trackers can add value to commercial projects. The potential gains from utilizing solar trackers become more apparent in large-scale commercial builds, where the scale and energy demands are significantly higher. The increased efficiency resulting from precise panel positioning can lead to substantial energy, which can offset the initial investment costs over time.
If you are considering solar trackers, you are welcome to learn about our single-axis solar tracking system. Please click here.